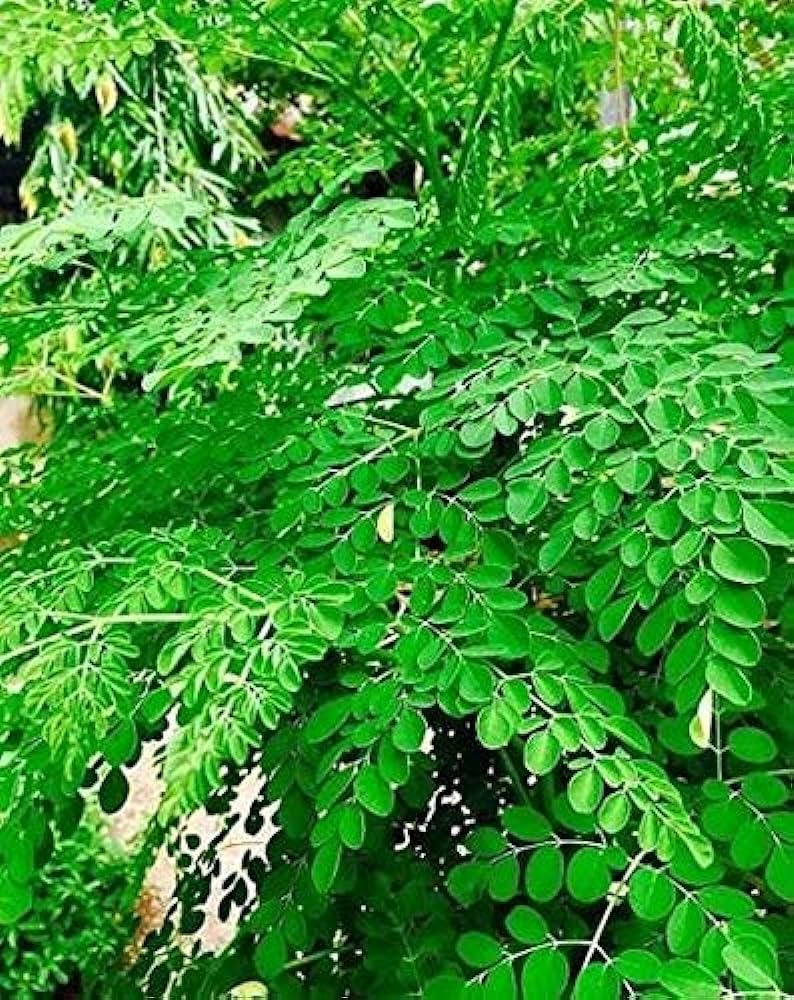
Sahjan
- Family : Moringa oleifera
- Local Names : mharic (shiferaw), Arabic (rawag), Bengali (sujina,sohjna,sajina), Burmese (dan-da-lun,dandalonbin), Cantonese (nugge), Creole Patois (benzolive tree), English (moringa tree,ben-oil tree,cabbage tree,clarifier tree,horse-radish tree,drumstick tree)
Description
- Moringa oleifera is a small, graceful, deciduous tree with sparse foliage, often resembling a leguminous species at a distance, especially when in flower, but immediately recognized when in fruit. The tree grows to 8 m high and 60 cm dbh. Bole crooked, often forked from near the base. Bark smooth, dark grey; slash thin, yellowish. Twigs and shoots shortly but densely hairy. Crown wide, open, typically umbrella shaped and usually a single stem; often deep rooted. The wood is soft.
- Leaves alternate, the old ones soon falling off; each leaf large (up to about 90 cm long), with opposite pinnae, spaced about 5 cm apart up the central stalk, usually with a 2nd lot of pinnae, also opposite, bearing leaflets in opposite pairs, with a slightly larger terminal leaflet. Leaflets dark green above and pale on the under surface; variable in size and shape, but often rounded-elliptic, seldom as much as 2.5 cm long.
- Flowers produced throughout the year, in loose axillary panicles up to 15 cm long; individual flower stalks up to 12 mm long and very slender; 5 pale green sepals 12 mm long, finely hairy, 5 white petals, unequal, a little longer than the sepals; 5 stamens with anthers, 5 without; style slender, flowers very sweet smelling. 4. Fruit large and distinctive, up to 90 cm long and 12 mm broad, slightly constricted at intervals, gradually tapering to a point, 3- (4-) angled, with 2 grooves on each face, light brown. It splits along each angle to expose the rows of rounded blackish oily seeds, each with 3 papery wings.
Ecology
Readily colonizes stream banks and savannah areas where the soils are well drained and the water table remains fairly high all the year round. It is quite drought tolerant but yields much less foliage where it is continuously under water stress. It is not harmed by frost, but can be killed back to ground level by a freeze. It quickly sends out new growth from the trunk when cut, or from the ground when frozen. Native range India, Malaysia, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Yemen
Tree Management
- Moringa is an extremely fast-growing tree, and within 1-3 months trees reach 2.5 m. Constant pruning of up to 1.5 m/year is suggested to obtain a thick-limbed and multibranched shrub. Trees are commonly grown for their leaves, and topping-out is useful to keep an abundant supply of leaves, pods and flowers within easy reach. M. oleifera responds well to mulch, water and fertilizer. Growth is stunted in areas with a high water table. It coppices and pollards well.
- Seed storage behaviour is orthodox; viability can be maintained for several years in hermetic storage at 3 deg. C with 5-8% mc. Seeds should be collected from well-developed pods, but difficulties arise because seeds drop continually.
- Readily colonizes stream banks and savannah areas where the soils are well drained and the water table remains fairly high all the year round. It is quite drought tolerant but yields much less foliage where it is continuously under water stress. It is not harmed by frost, but can be killed back to ground level by a freeze. It quickly sends out new growth from the trunk when cut, or from the ground when frozen.
- M. oleifera is easily established by cuttings or by seeds. Seeds can be sown either directly or in containers. No seed pretreatment is required and seeds sprout readily in 1-2 weeks. Plants raised from seed produce fruit of unpredictable quality. Shield budding is successful, and budded trees begin to bear in 6 months and continue to give a good crop for 13 years. As it is essentially a vegetatively propagated crop, breeding methods like single-plant selection, mass selection and exploitation and maintenance of vigour are transgressive. Stem cuttings are usually preferred because they root easily. When grown for its roots, the seeds are sometimes planted in rows like vegetables.
Timber
The wood is very soft and light and is useful only for light construction work.
Medicine
Moringa seeds are effective against skin-infecting bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. They contain the potent antibiotic and fungicide terygospermin. The alkaloid spirachin (a nerve paralysant) has been found in the roots. Even when free of bark, the condiment in excess may be harmful. A decoction of the flowers is used as a cold remedy. The gum is diuretic, astringent and abortifacient and is used against asthma. Oil of Ben is used for hysteria, scurvy, prostate problems and bladder troubles. The roots and bark are used for cardiac and circulatory problems, as a tonic and for inflammation. The bark is an appetizer and digestive. The iron content of the leaves is high, and they are reportedly prescribed for anaemia in the Philippines.
Gum or resin
When the tree is injured, the stem exudes a gum that is used in calico printing, as a condiment, and for stomach and bladder ailments. The mucilaginous gum has a bland taste and belongs to the hog series of gums.